Dopamine Hub Synapses in the striatum: a new hot spot for dopamine transmission?
How is the conversation between neurons organized in the brain? Through 2 recent articles, part of this organization between the dopamine and surrounding neurons at synapses is described.
Synapses are points of contact between neurons, essential for the proper functioning of the brain. In the brain, neurons are of 2 main types. The effector neurons ensure a rapid and local transmission of information, either excitatory or inhibitory, while the modulatory neurons, few in number, affect large regions of the brain over longer periods of time. Modulatory neurons using dopamine are very important for the tuning of motor control, motivation and reward perception.
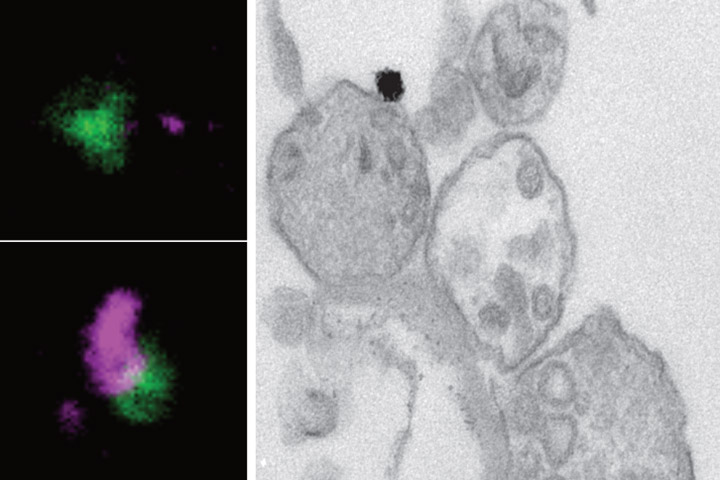
In their studies, the researchers established the first selective purification of dopaminergic synapses in the striatum that allowed us to identify 2650 proteins, 57 of which were specifically enriched. In contrast, few messenger RNAs (encoding proteins) are selectively detected, suggesting that local translation of proteins is not a major mechanism at the axons of dopaminergic neurons. In addition, they have identified a new structure where dopaminergic synapses physically interact with other classical synapses and affect the composition of the latter.
These “Dopamine Hub Synapses” may mediate dopamine neuromodulation on striatal neuronal circuits, fueling the debate between volume and synaptic models of modulatory transmission. Within this new conceptual framework, future research will provide a detailed understanding of the cellular mechanisms by which dopamine modulates voluntary movements or reward-prediction based learning. This is crucial as many pathologies such as Parkinson’s disease, addiction and schizophrenia are linked to dopamine dysfunction.
The publication in Nature Communications is a collaboration between staff from IINS, BIC and Nutrineuro. (see reference below).
The publication in Cell Reports is a collaboration between Etienne Herzog ad 2 teams of Columbia University (New York).
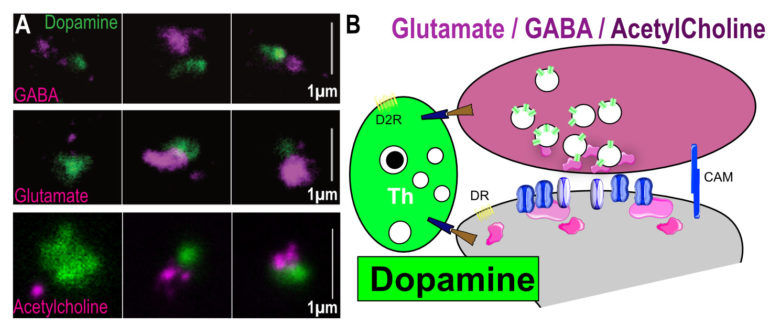
A: Isolated dopamine synaptic terminals (green) bind to GABA (top, magenta), Glutamate (middle, magenta) or Acetylcholine (bottom, magenta) positive terminals. Scale bar 1µm. B: Model cartoon of dopamine hub synapses. DR/D2R : Dopamine Receptors; CAM: Cell Adhesion Molecule: Th: Tyrosine hydroxylase (dopamine biosynthesis).
A synaptomic analysis reveals dopamine hub synapses in the mouse striatum
Nature Communications
2022 Jun 3;13(1):3102. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-30776-9.
Vincent Paget-Blanc # 1, Marlene E Pfeffer # 1, Marie Pronot # 1, Paul Lapios 1 , Maria-Florencia Angelo 1 , Roman Walle 2 , Fabrice P Cordelières 3 , Florian Levet 1 3 , Stéphane Claverol 4 , Sabrina Lacomme 3 , Mélina Petrel 3 , Christelle Martin 1 , Vincent Pitard 5 , Véronique De Smedt Peyrusse 2, Thomas Biederer 6 , David Perrais 1 , Pierre Trifilieff 2 , Etienne Herzog 7
1 Univ. Bordeaux, CNRS, Interdisciplinary Institute for Neuroscience, IINS, UMR 5297, F-33000, Bordeaux, France.
2 Univ. Bordeaux, INRAE, Bordeaux INP, NutriNeuro, UMR 1286, F-33000, Bordeaux, France.
3 Univ. Bordeaux, CNRS, INSERM, Bordeaux Imaging Center, BIC, UAR 3420, US 4, F-33000, Bordeaux, France.
4 Univ. Bordeaux, Plateforme Proteome, 33000, Bordeaux, France.
5 UB’FACSility CNRS UMS 3427, INSERM US 005, Univ. Bordeaux, F-33000, Bordeaux, France.
6 Department of Neurology, Yale School of Medicine, New Haven, CT, 06511, USA.
7 Univ. Bordeaux, CNRS, Interdisciplinary Institute for Neuroscience, IINS, UMR 5297, F-33000, Bordeaux, France.
# Contributed equally.
Subcellular and regional localization of mRNA translation in midbrain dopamine neurons
Cell Reports
38-2, (2022). doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.110208
1 Department of Systems Biology, Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York 10032, NY, USA; Medical Scientist Training Program, Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York, NY 10032, USA; Department of Psychiatry, Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York, NY 10032, USA.
2 Department of Systems Biology, Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York 10032, NY, USA.
3 Interdisciplinary Institute for Neuroscience, Université de Bordeaux, Bordeaux, France; Interdisciplinary Institute for Neuroscience, CNRS UMR 5297, Bordeaux, France.
4 Medical Scientist Training Program, Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York, NY 10032, USA; Department of Psychiatry, Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York, NY 10032, USA.
5 Department of Psychiatry, Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York, NY 10032, USA; Division of Molecular Therapeutics, New York State Psychiatric Institute, New York, NY 10032, USA.
6 Interdisciplinary Institute for Neuroscience, Université de Bordeaux, Bordeaux, France; Interdisciplinary Institute for Neuroscience, CNRS UMR 5297, Bordeaux, France. Electronic address: .
7 Department of Neurology, Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York, NY 10032, USA; Department of Psychiatry, Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York, NY 10032, USA; Department of Pharmacology, Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York, NY 10032, USA; Division of Molecular Therapeutics, New York State Psychiatric Institute, New York, NY 10032, USA; Aligning Science Across Parkinson’s (ASAP) Collaborative Research Network, Chevy Chase, MD, USA. Electronic address: .
8 Department of Systems Biology, Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York 10032, NY, USA; Department of Biochemistry & Molecular Biophysics, Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York, NY 10032, USA; Sulzberger Columbia Genome Center, Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York, NY 10032, USA; Aligning Science Across Parkinson’s (ASAP) Collaborative Research Network, Chevy Chase, MD, USA. Electronic address: .
* Corresponding authors
Contact
Etienne Herzog
IINS
Equipe: Membrane Traffic at Synapses
Last update 16/06/22
